The following example is used to explain the procedure to follow:
Problem:
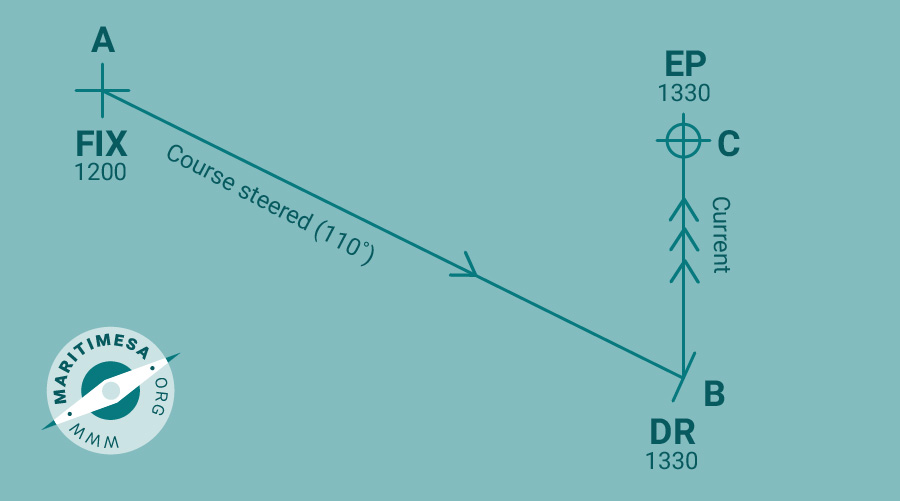
From an observed position at 1200 a vessel steers 110° (T) at 10 knots. The current is setting 350° (T) at 2 knots. Determine the estimated position for 1330.
Solution:
- Plot the true course from the 1200 position.
- Plot the DR position for 1330.
- Calculate the drift for the time interval (2 x 1½)miles. This will constitute the current vector at 1330.
- Draw the current vector from the DR position.
- The EP will be at the end of the current vector.
- Plot the EP.