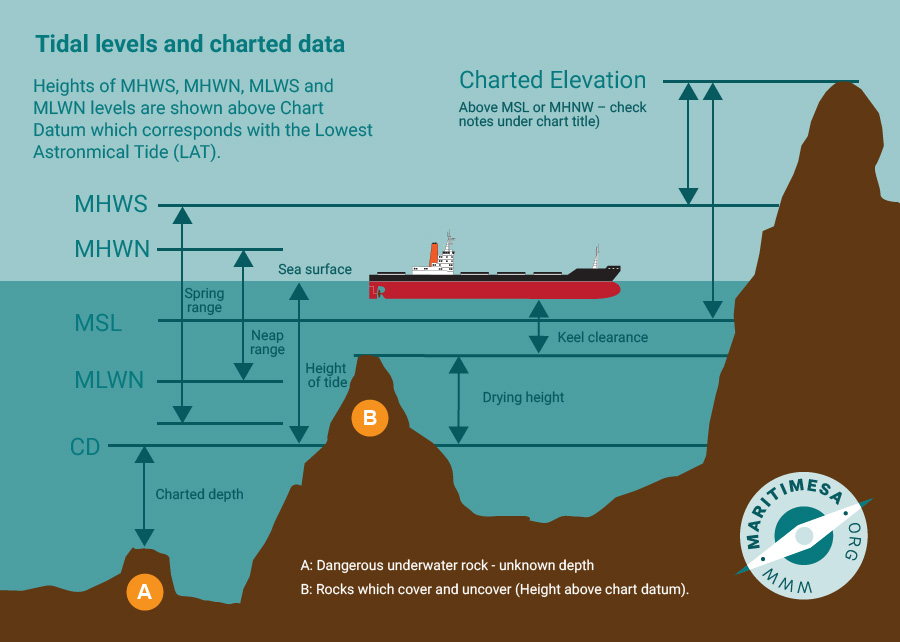
Highest Astronomical Tide (HAT) and Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT).
These levels are predicted to occur under average meteorological conditions and under any combination of astronomical conditions. They will not be reached every year. They are also not the extreme levels that can be reached, as storm surges and other meteorological conditions can cause considerably higher and lower levels to occur.
Mean High Water Springs (MHWS) and Mean Low Water Springs (MLWS).
The height of mean high water springs is the average over a year of the heights of two successive high waters during those periods of 24 hours (once every fortnight) when the range of the tide is greatest. Mean low water springs is the average height obtained from two successive low waters during the same period.
Mean High Water Neaps (MHWN) and Mean Low Water Neaps (MLWN).
The height of mean high water neaps is the average over a year of the heights of two successive high waters during those periods of 24 hours (once every fortnight) when the range of the tide is least. Mean low water neaps is the average height obtained from two successive low waters during the same period.
Mean Sea Level (MSL).
This is the mean of the heights of MHWS, MLWS, MHWN and MLWN.
Tidal cycle.
The values of MHWS, MLWS, MHWN and MLWN vary from year to year in a cycle of approximately 18.6 years.
For a graphical presentation of the relationship between the above definitions, the following diagram shows
the physical relationship between the various defined levels of tide and the chart datum: