Vessel identities.
Vessels identify one another either by their name or international call sign. The name is obviously given to the ship when it is launched. The call sign is allocated by the department issuing the vessel’s radio licence/certificate, usually by the country in which the ship is registered. A call sign is a sequence of letterers/figures issued by the telecommunications authority of a country to vessels registered in that country. Personal names of individuals aboard the vessel are not used.
Time.
Time mentioned or used in a signal is always written in the 24 hour clock format, ie 2 o’ clock in the morning is written as 0200, whilst 2 o’ clock in the afternoon is written as 1400. Furthermore to avoid confusion with the varying time zones, the transmission time of all signal traffic is entered and recorded in GMT (Greenwich Mean Time).
Commonly used words or phrases used when communicating (voice communicating procedure).
Words/phrases & their meaning:
All after; All before; Word after; Word before.
These are words used when one vessel asks the other to repeat parts of a message or when one vessel is repeating parts of a message.
In figures; In numbers.
These are used when a vessel wants to inform the receiving ship that what follows are numbers.
Correct; Correction.
Used when correcting or indicating something is correct in a message.
Say again; Repeat.
Used to ask for or give a repeat of a message.
Read back.
Used when a vessel asks another vessel to read back his message to ensure that he has received it correctly.
I spell.
Used when a vessel wants to spell out a word in a message.
Over.
When the calling ship wants the other vessel to reply to his call.
Out.
When one vessel is finished passing his message and he does not want the other vessel to answer.
Wait.
When the receiving vessel requires some time to answer a query posed by another vessel.
Stand by.
When one vessel tells the other to wait further communication.
Roger.
Means “yes” or “affirmative”.
Radio check.
When one vessel wants to know whether his or the other vessel’s radio is working properly, he will ask for a radio check.
Text.
Means plain language.
Traffic.
On a radio circuit this means messages.
Working frequency.
This is the frequency that is used to pass traffic between vessels.
Calling frequency.
This is the frequency used to establish communications with another vessel.
Phonetic alphabet.
In order to aid clarity and avoid confusion when spelling over a radio circuit, an internationally accepted phonetic alphabet is used, ie the normal pronunciation of the letters b, c, d, and e all sound very similar but using the phonetic alphabet they would be pronounced as Bravo, Charlie, Delta, Echo. As you can see they sound completely different. The table below contains the Morse symbols also gives the phonetic alphabet.
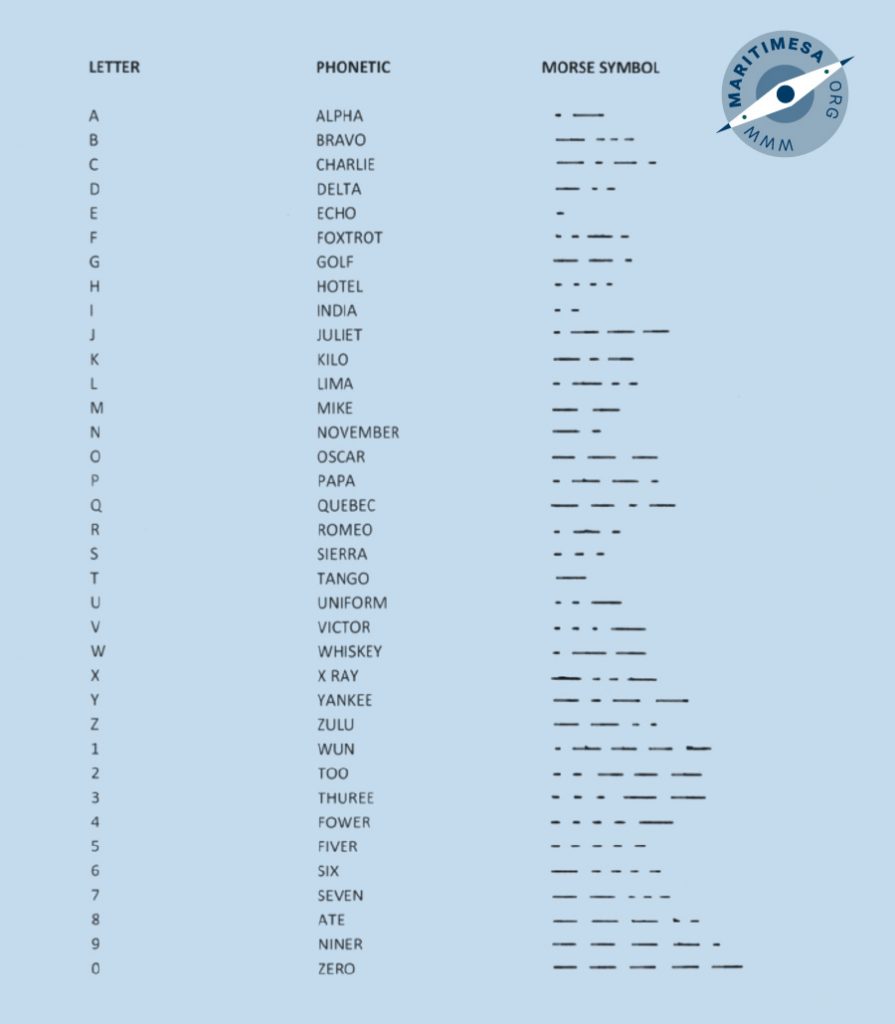
Phonetic alphabet/Morse code table.


