Dry dock (graving dock). This is an excavation faced with solid masonry which is connected with a harbour, river or basin. The entrance is closed with a sliding caisson, a floating caisson or dock gates. Water is admitted through special valves until the level of the water in the dock is the same as that outside. The entrance is then opened, the ship is floated in and the dock is then closed. The water is then pumped out, leaving the ship resting on special keel blocks and supported by breast and bilge shores(wooden beams) to ensure she remains upright.

Typical graving / dry dock.
Wet dock. This is a floating watertight dock which can be submerged sufficiently to receive a vessel by flooding the pontoon tanks which form the bottom of the dock. When the vessel has been floated in and secured, the tanks are pumped out until the vessel and the pontoon deck is dry.

Wet / floating dock.
Patent slip. This consists of a sloping runway of concrete, extending some distance below the low water mark, on which rails are laid. A cradle, fitted with a wheeled carriage, is run out to receive the vessel when there is sufficient water. The vessel and the cradle are hauled up the runway by winch or capstan until they are clear of the water.

Patent slip.
Hydraulic synchro lift. This consists of a platform on which a craft is positioned and is capable of being raised or lowered by a number of synchronised hydraulic winches.

Synchro-lift in Durban harbour (the white objects are covers for the electric winches which lift the platform bearing the vessel). The vessel in the foreground was raised and shifted off the platform leaving it available for further vessels. (SA Navy).
Jetty. A platform which is built out from the shore on piles so that there is sufficient water alongside to berth ships.

Jetty for small craft.
Pier. A narrow jetty built of masonry on piles, usually extending seawards at right angles to the shoreline. It is either used as a breakwater or for berthing ships.

Pier.
Quay. This is a concrete structure inside harbours alongside which vessels are berthed.

A quay.
Mole or breakwater. This is a long pier of heavy masonry or concrete built on the seaward side of a harbour to protect the harbour from the action of the sea.

A breakwater ashore.
Dolphins. Mooring posts consisting of groups of piles driven into the bottom of the harbour.

A line of dolphins connected by a pier.
Catamaran. A strongly constructed wooden or steel raft placed between ships or between a ship and the jetty to avoid damage to the ship and the jetty. The sides are protected by thick rubber tubing.

Catamaran fender.
Fenders. Fenders are used to protect the ship’s side when coming alongside another vessel or the quay/jetty. They could be made out of rattan (a type of cane/wicker) or rubber. They could be shaped like a doughnut or a short large sausage (inflatable type). Sometimes old (used) rubber tyres are used .
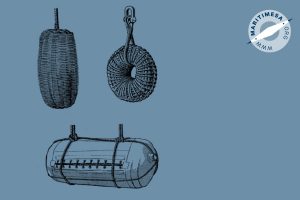
Wicker and pneumatic fenders.


